The research in Prof. Shuqiang Jiao group is greatly interested in electrochemical metallurgy and material physical chemistry fields, with the emphasis on new extraction and refinement approach of metal titanium, comprehensive utilization of complex titanium mineral resources, inert anode materials, molten oxides electrolysis, electrochemical capture and transformation of CO2 in molten salts, novel aluminum-ion batteries, and so on.
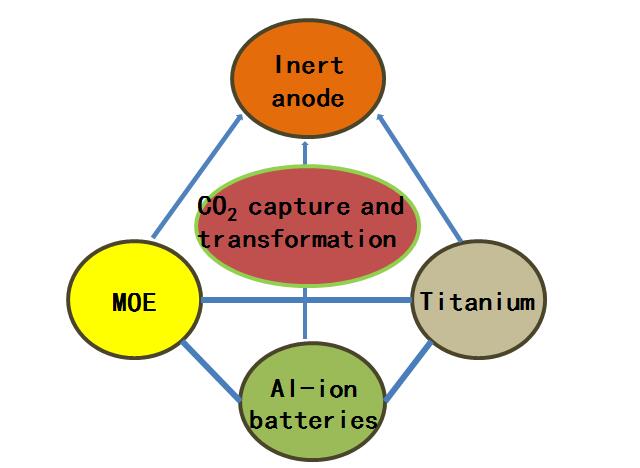
The achievements we have made in the field of physical chemistry of metallurgy will be critical for the group research in forthcoming years. Future work in the group will primarily focus on Ti refining, electro-transformation of CO2, and novel cathode materials and electrolytes for high-performance batteries. Significant efforts will also be devoted to developing practical and industrial high-purity titanium and energy storage devices.